A Complete Guide to Alternative Proteins
The impacts of climate change are increasing continuously, and if you want to help stop it, you can do it in many ways. Choosing alternative proteins over traditional proteins is one of the easiest ways.
The world of proteins has diversified, and you can find several protein sources besides meat. With the increase in funds and growth in the industry, innovative options are introduced beyond plant-based proteins.
Most people use the term plant-based for all alternative protein sources, but it is a limiting term as it does not cover the full spectrum of animal-free food.
Read More: High Protein Milk Alternative
What Are Alternative Proteins?
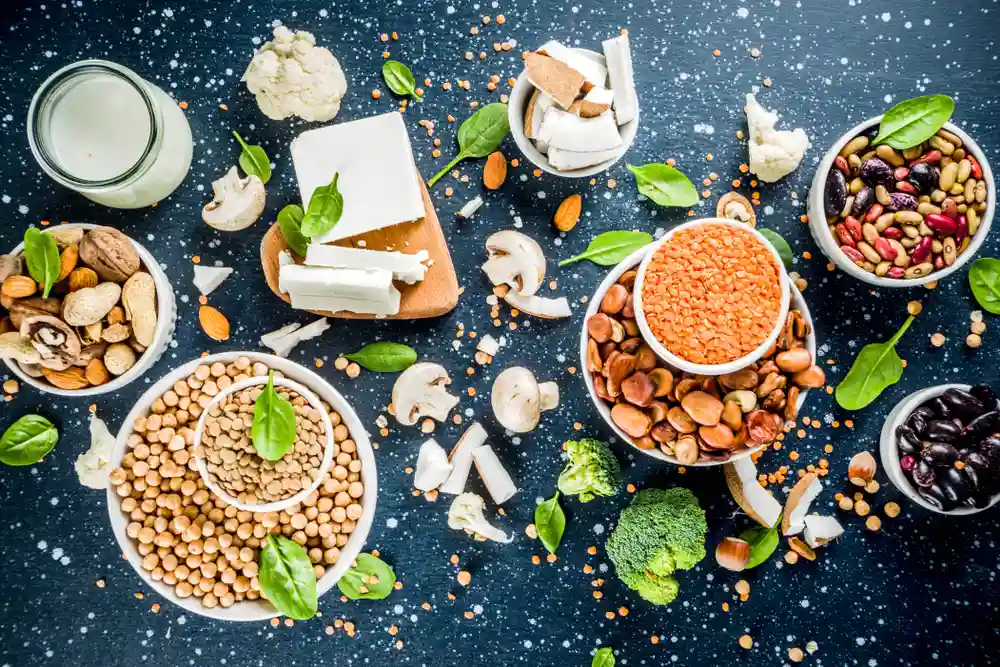

Let’s state the basics to get a clear understanding of this term. Alternative protein or alt protein is a term used for foods, beverages, and ingredients that have protein derived from non-animal sources. They are usually plant-based and other food technology alternatives to animal proteins.
All humans need proteins to build muscles, get energy, or repair cells, and usually, they take it from animals or plants.
Over time this trend has changed, and people are now shifting to alternative proteins for several reasons, such as to avoid animal cruelty, help climate change and improve their eating habits.
Top Trending Alternative Proteins:
With the increasing demand for alt proteins, new products are introduced. Here are four rapidly growing alt protein markets:
Plant-Based Protein :
Plant-based proteins are the most popular and well-known of all modern alternative protein sources. They have become prevalent in the food industry because consumers demand environment-friendly alternatives to animal proteins.
Most often, people use to phrase plant-based when they are consuming any alternative in the animal-free space, but it is not the true meaning of plant-based. Let’s take a deeper dive to understand what plant based-alternatives mean.
Often replacing animal proteins in foods like chicken nuggets or burgers with proteins from plant sources.
For example, if a pea plant is a source, protein is isolated from it while leaving everything else behind.
People can eat raw plants to get protein, but many still crave the taste of meat and dairy products. That is why food technologists are innovating new products similar in taste to meat and dairy products.
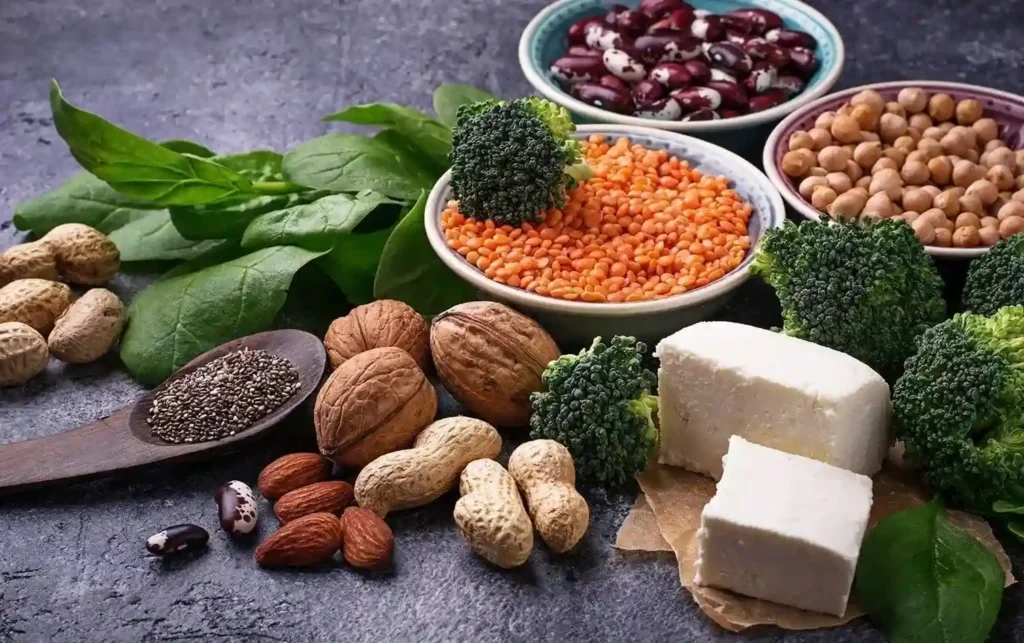

Soybean, oilseeds, and legumes are some common protein-rich plant sources. They usually contain more fiber and less saturated fats when consumed raw. However, their health benefits may be affected when they are processed to produce meat alternatives.
Other than plant-based proteins, plant-based beverages like milk are also getting popular globally. People now consume soy milk, oat milk, and almond milk, as high-protein milk alternatives. We can say that now you can get plant-based versions of most foods and drinks.
Fungi-Based Alternative Proteins :
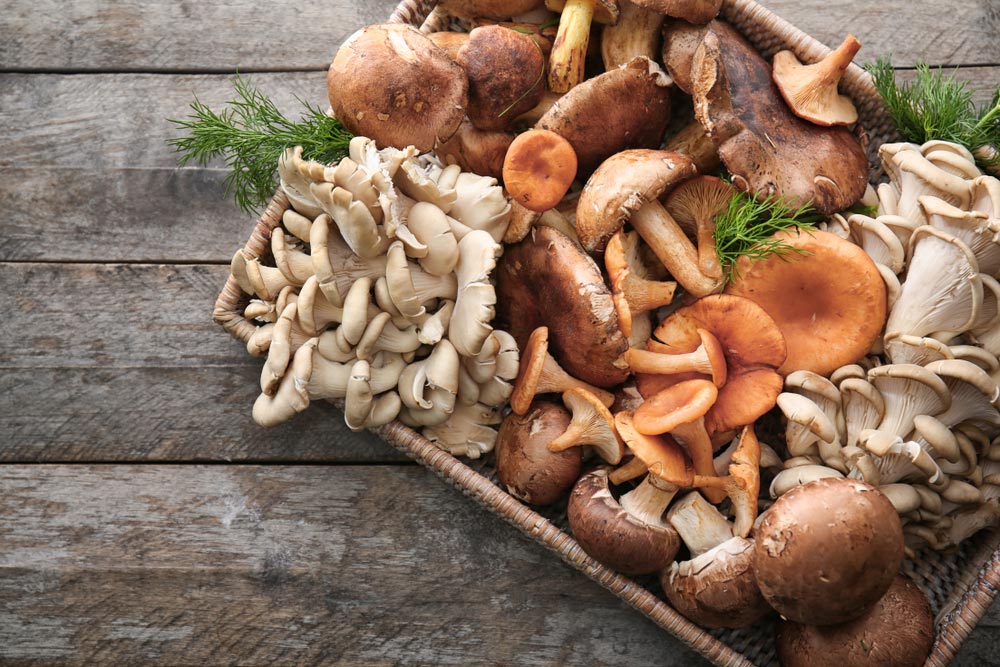

In the past, scientists considered fungi a type of plant, but now we all know that fungi have their own kingdom and are more closely related to animals than plants.
Even though they are still stocked in the plant section of grocery stores. If you want to understand the world of fungi, it is essential to learn about mycelium. When you think of Fungi, only mushroom caps may come to your mind. However, it is only one part of fungi and known as the fruiting body.
Mycelium is a fibrous structure in the fungus, and it mostly remains hidden, spreading thousands of miles underground. It is made up of hyphae, thread-like strands that grow into a dense fibroids structure.
Many proteins obtained from fungi are inherently rich in nutrients. They contain huge amounts of protein and fiber and are low in saturated fats. In plant-based proteins, an existing protein is converted to another form of protein, but fungi-based proteins are a source of net-new protein.
For example, fungi convert carbohydrates into proteins containing all amino acids, including nine essential ones.
Most animal proteins contain the right combination of amino acids, so consumers get all the nine they need. But vegans and vegetarians need to use varied sources of plant proteins or mix and match non-animal sources to get the right amount of amino acids.
One good example is the combination of rice and beans, each having an incomplete amino acid profile, but together they can provide all nine essential amino acids.
The number of companies providing fungi-based proteins is increasing to provide sustainable food production and beat the challenge of a growing population and climate change.
How Fungi-Based proteins Are Produced?
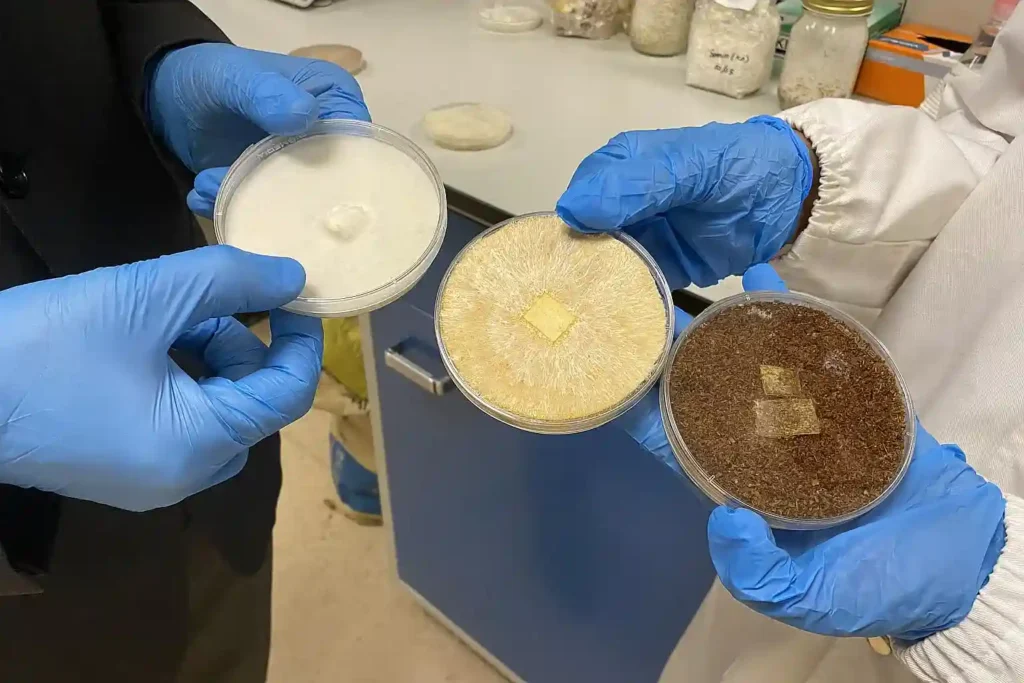

Some food manufacturers have manufactured nutritional fungi by fermenting filamentous fungi. The natural fibrous structure of mycelium helped manufacturers in mimicking the texture of meat.
However, they are also used to produce creamy liquids and then dried into powders like flour. It helps manufacturers bring various products to the alternative proteins market.
Different types of fermentation methods are used to produce plant and animal proteins. For example, submerged, liquid-air interface fermentation, and solid-state fermentation. The level of proteins produced varies with the type of fermentation.
Liquid air interface fermentation is a unique and simple type of fermentation in which fungi grow in vertical racks of trays indoors. In contrast, large tanks are required to grow fungi in submerged fermentation.
Read More: FOOD TECH TRENDS AND INNOVATIONS IN 2022
Algae-Based Protein :

Although algae have been researched and consumed for several years, now algae-based proteins are becoming popular in the alt protein market. Companies are using algae to produce algae-based proteins.
In order to do so, they extract a microalga and ferment it to make an ingredient that is further combined with flavours to make a final food product. When you study, you will find that different kinds of algae are used in different applications.
Since the micro algae-based foods are still in the initial research stage and are being produced only at a small scale, there are many unknown things about isolating and scaling algae-based proteins.
One challenge this alt protein faces is that algae do not have a neutral color, taste, or smell. Without that, making it a widely accepted alternative to animal proteins is difficult. As the research in this field grows, the advantages and disadvantages of producing algae-based proteins will become clear.
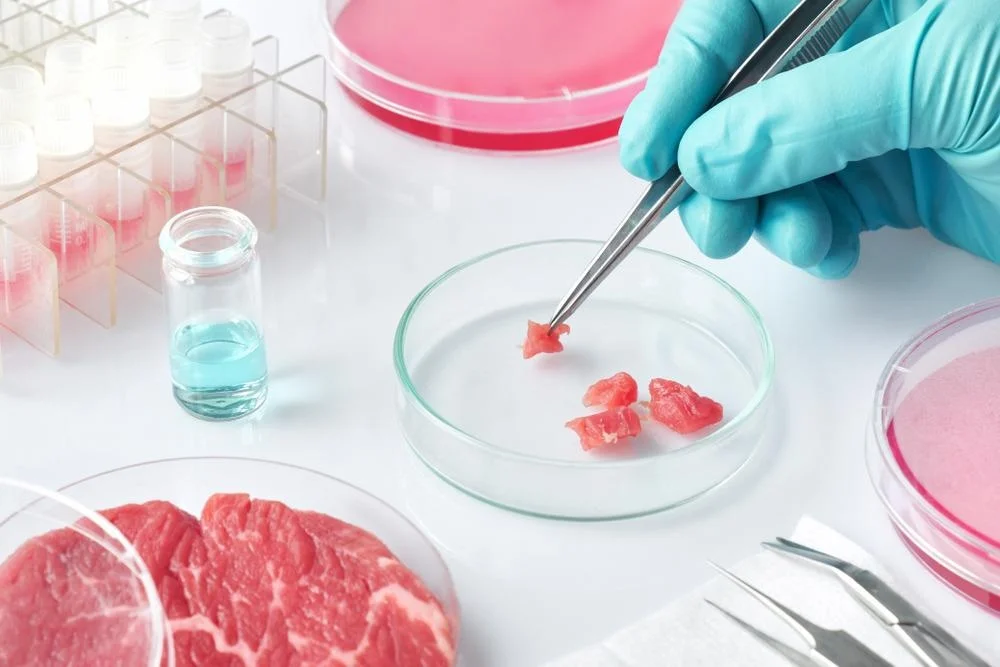
Lab Grown Meat An Alternative protein :
There is much debate on what to call this new alternative to animal protein. So, if you are new to this field, people use different names for lab-grown meats, such as cell-based meat, cultivated meat, or clean meat. No matter what it is called, it is an alternative protein manufactured by growing a few animal cells in a lab into fully edible meat.
Companies are producing meat from fish, mammals, and even specific organs of animals. Moreover, there is no need for large plants to produce lab-grown meat.
The best thing is that the resulting product tastes like animal meat because it is grown directly from animal cells. Furthermore, lab-grown meat removes the need to slaughter animals to get meat, thus reducing many diseases that come from meat from slaughterhouses. It also helps decrease the greenhouse gasses emitted from rearing livestock.
Currently, most lab-grown meat companies are in the testing phase, with a few in the market. Also, the cost of lab-grown meats is very high at this time as compared to traditional meat products.
Until companies get regulatory approvals for the mass production of cultivated meat, these costs will likely remain high.

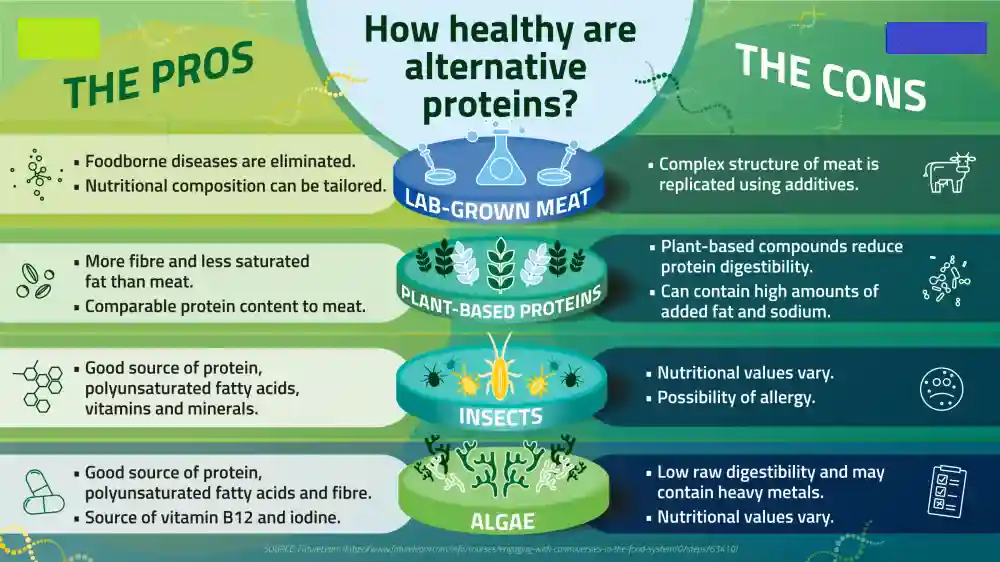
Pros And Cons Of Alternative Proteins :
alternative proteins Pros
alternative proteinsCons
- Plant-based proteins contain reduced content of harmful bacteria.
- The nutritional composition of lab-grown meat can be tailored to increase health benefits.
- Alternative proteins require less land and water for production.
- Alt proteins are rich in fiber and contain less saturated fats and cholesterol.
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions and land use compared to animal rearing.
- The human body does not readily absorb plant plants.
- Vegetarians usually lack vitamin B12.
- Complex meat products are difficult to mimic, such as steaks.
- Cultured meat needs more energy and cost for large-scale production.
- Some algae-based proteins have low digestibility when consumed raw.
- Possibility of allergy in people. For example, some people are allergic to gluten or other plant proteins.
Bottom Line :
Our planet’s future directly relies on our food system’s future. If we do not find innovative and sustainable ways for food production, food insecurity will increase, and it will become difficult to survive on earth.
In such situations, it is exciting that the new alternative protein sources are playing a role in nourishing our growing population while reducing the effects of climate change.
Whether you choose plant-based, fungi-based, lab-grown, or algae-based proteins, you choose a sustainable option that is better for you and your planet.