What Is Biodiversity And Why Is It Important?
The air you breathe, the food you eat, and the water you drink all depend on biodiversity. It is the name we give to all the living things on Earth, including plants and people, to baboons and bacteria.
Our planet is incredibly full of a range of life, and every living thing exists within its communities or ecosystems.
All the living things on Earth and their interaction with each other is what makes Earth a perfect place to live. But it is in crisis due to human beings.
What Is Biodiversity?
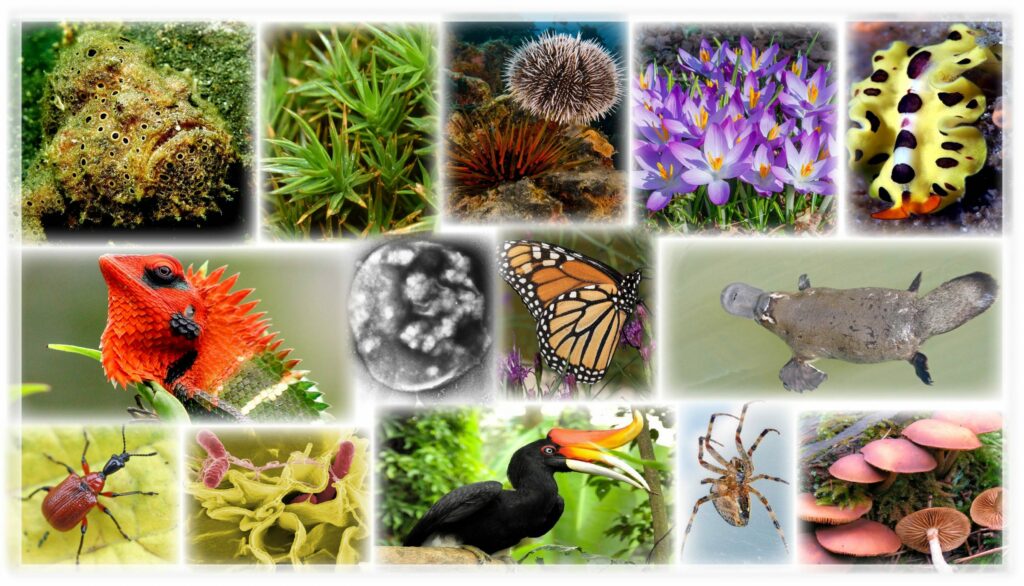

It is defined as life on Earth in all its forms and interactions of all living things with each other. It may sound bewilderingly broad, but that’s because it is really a broad term. We can say that it is one of the most complex features of our planet, and at the same time, it is the most essential.
According to Professor David Mcdonald, “without biodiversity, there is no future for humanity.”
The term was invented in 1985 as a contraction of biological diversity. But now, the losses of biodiversity are becoming visible all across the globe, ultimately resulting in climate change.
More formally, biodiversity comprises different levels, from genes, individual species, communities, and entire ecosystems such as coral reefs and forests.
In these ecosystems biodiversity, and life interplay with the physical environment. These innumerable interactions have made Earth habitable for billions of years.
Now, if we see biodiversity in a more philosophical way, it represents the knowledge that humans obtained from the evolving species over millions of years and how to survive through the varying environmental conditions of our planet.
After deep research and analysis, experts have warned that humans are currently burning the library of life.
Why is Biodiversity Important?
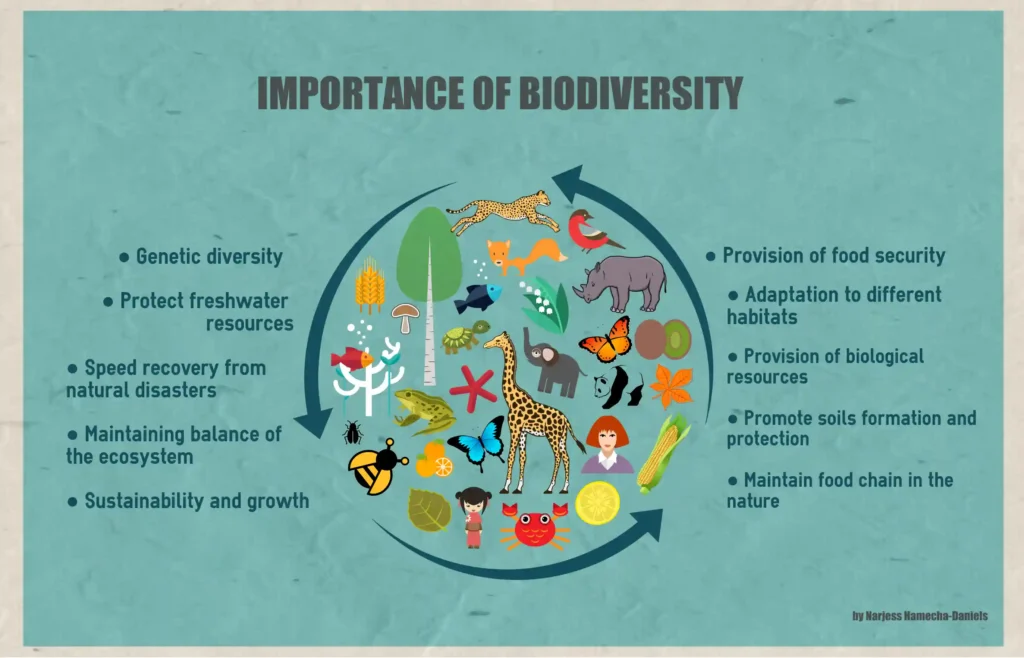
Biodiversity Importance:
Biodiversity is essential for your health, safety, livelihood, and business. But it is declining at an ever faster rate in human history. The changing behavior and activities of human beings have resulted in the loss of 83% of wild mammals and almost half of the plants.
It can result in the collapse of the entire ecosystem on Earth. Humanity needs to stop the pace of wildlife extinction or be ready to face its consequences.
Currently, more than 1 million species are at risk of extinction, and experts say that the stakes have never been much higher.
Biodiversity Ensures Food Security :
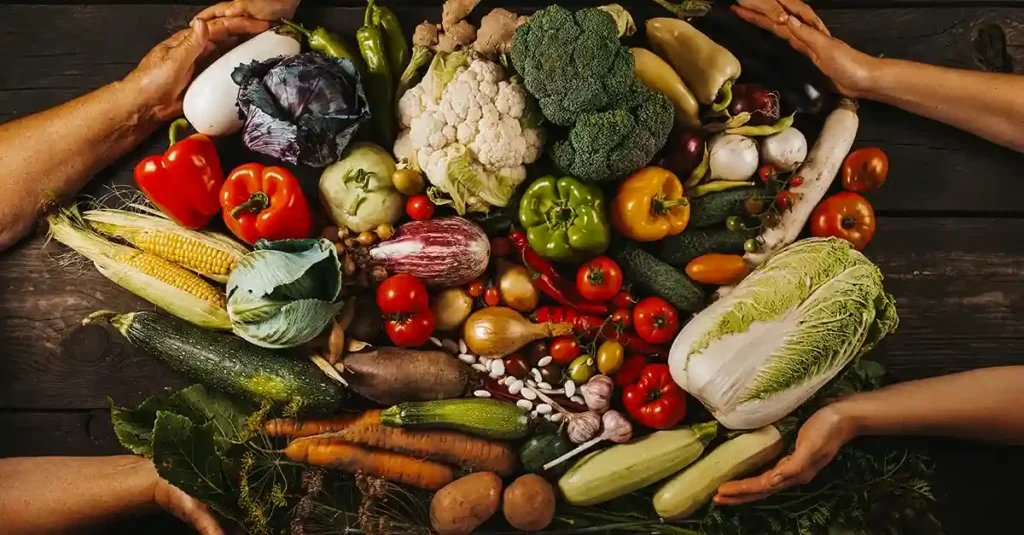

One important thing you need to understand about biodiversity is that it supports global nutrition and food security.
Millions of species work together and provide us with a large variety of vegetables, fruits, and animal products that are essential for a healthy and balanced diet. But all of them are increasingly under threat.
Every country in the world has local produce, including crops and grains. These crops are adapted to the local cl conditions and are resilient to extreme weather. In the past, this product was a great source of micronutrients for the local population.
Unfortunately, processed foods, simplification of diets, and poor access to food have led to poor-quality diets. That is why one-third of the world population now suffers from micronutrient deficiency.
Three crops, wheat, rice, and corn, provide 60% of the total plant-based calories. As a result, we have less resilience in our food supply chain. The varieties of rice in Asia and Thailand have reduced from tens of thousands to dozens.
We must ensure this knowledge is part of our modern agriculture system. It can help to prevent diseases due to nutrient deficiency and reduce the environmental impact of feeding humans.
Less Biodiversity Means More Diseases :
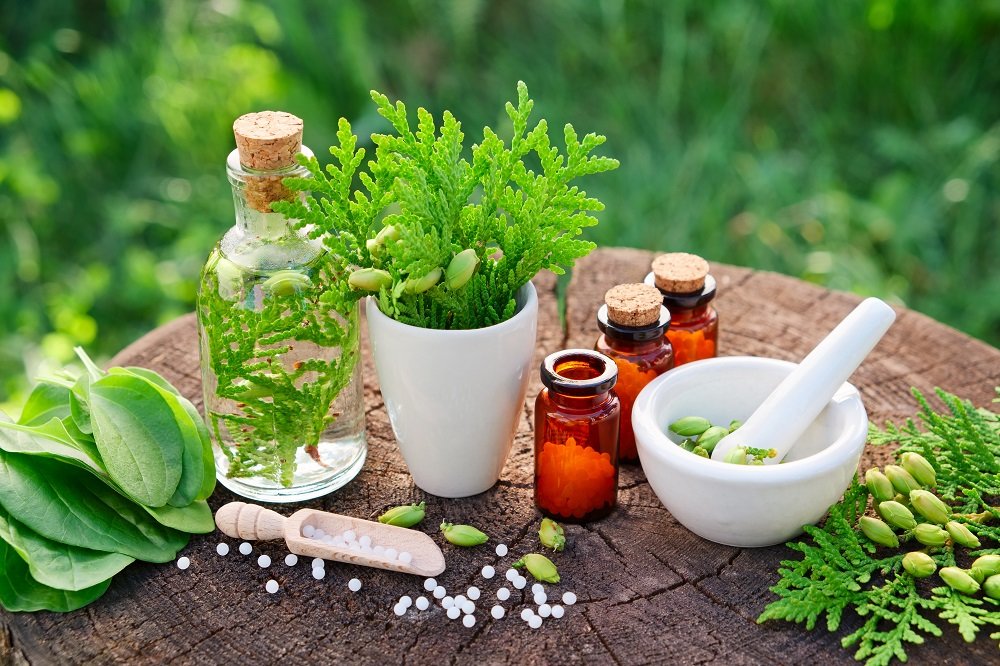

High rates of biodiversity are also linked with the increase in human health. First, plants are a major part of many medicines.
Biodiversity example, 25% of drugs used in medicines are obtained from rainforest plants 70% of cancer drugs are natural or produced synthetically inspired by nature. It shows that every time any plant species goes extinct we lose a potential medicine source.
Second, biodiversity due to protected natural areas has been related to lower chances of diseases such as malaria and Lyme disease.
According to a study, 60% of infectious diseases emerge from animals, and 70% of new infectious diseases come from wildlife.
As human activities are disturbing the natural world through urbanization and deforestation, the number and size of ecosystems are reducing.
Biodiversity Is Beneficial For Business :
According to the World Economic Forum’s recent report on nature risk, more than half of the world’s GDP is directly or indirectly dependent on nature. So many businesses are at risk due to the increase in loss of biodiversity.
Global sales of pharmaceuticals based on natural materials are worth about $75 billion per year, while some natural wonders like coral reefs are essential for tourism and food.
There is a great potential for economic boost and resilience with the growth of biodiversity. You can find solutions to conserve biodiversity. With every dollar you spend on nature restoration, you can get $9 playback.
Since we are talking about the economy, keep in mind that protecting biodiversity also protects jobs.
According to the UN, jobs in industries like forestry, agriculture, and tourism are also linked to a healthy environment.
Biodiversity Is Linked To Healthy Soil And Clean water:
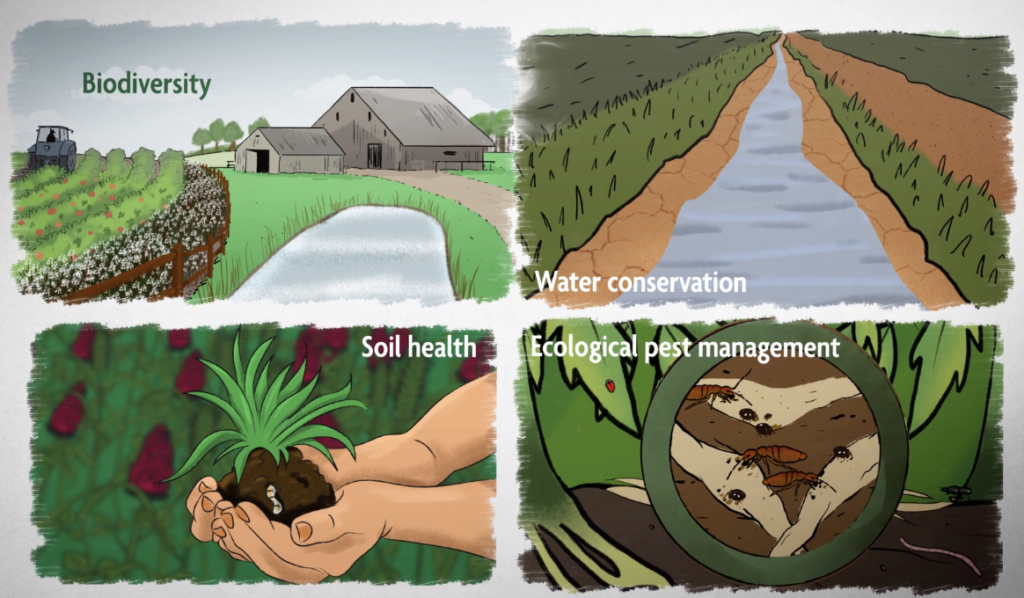
The soul is an essential part of the environment offering numerous benefits such as it filters water, breaks down organic matter, prevents erosion, and providing nutrients to plants. Without healthy soil, our planet will be a desolate rock.
What keeps soil healthy is its diversity. It is one of the most biodiverse ecosystems. Soil contains everything from bacteria to fungi and worms to spiders. If any one of those organisms is threatened, it will impact the health of the soil.
Water is essential for every living thing, so its cleanliness is vital. Biodiversity also plays a role in it. Nitrogen pollution is one of the most significant causes of water pollution.
Naturally occurring algae in water help in cleaning nitrogen in water channels. The more algae species in the rivers and water channels, the more the water is free from nitrogen.
keeps Our Planet Habitable:
Biodiversity makes our planet liveable. Biodiverse ecosystems help us by providing nature-based solutions that protect us from natural disasters such as storms and floods, regenerate soil, and filter water.
Therefore, the protection and restoration of natural ecosystems are crucial in to fight against natural disasters. Moreover, nature-based solutions also provide cost-effective ways to mitigate carbon dioxide resulting in global warming.
Biodiverse ecosystems support unlimited forms of life, including humans. Unfortunately, humans are the major cause of the reduction in biodiversity.
We have destroyed a huge number of trees, polluted our air, and contributed to the extinction of many species.
If we do not stop these habits and ignore the measures to protect biodiversity, it is no doubt that the Earth will become inhabitable very soon.
Read More: FOOD TECH TRENDS AND INNOVATIONS IN 2022
How Do Humans Effect Biodiversity?

Humans are impacting our planet’s biodiversity in many ways, both accidentally and deliberately.
The biggest threat to biodiversity till now has been the way humans changed the natural habitats to make way for natural resources, but as climate change is getting worse, it has increasing impacts on ecosystems.
The direct cause of loss in biodiversity is land use change, resulting in about 30% of biodiversity decline globally. The second significant cause is overexploitation of things like timber, food, and medicines which drives a 20% decline.
The third most significant reason for the reduction in biodiversity is climate change which, along with pollution, counts for a 14% decline. Invasive alien species cause an 11% decline.
Some studies predict that climate change will become the primary factor in biodiversity loss in the coming decades. With the increase in human population, the demand for natural resources is also increasing.
This increase in per capita consumption has meant that more natural habitats will be used for mining, agriculture, industrial infrastructure, and urbanization.
Here are key areas of human activities causing biodiversity loss:
- Deforestation results in the loss of tropical rainforests that are rich in biodiversity.
- Pollution is also a reason that impacts natural habitats. For example, the widespread use of pesticides and fertilizers results in water pollution affecting natural habitats in rivers and the ocean.
- Habitat loss is due to human activities such as cutting trees and using that space for housing societies or industrial infrastructure.
- It is estimated that half of the species in danger are threatened by agriculture.
- Water catchments such as dams used for irrigation and other purposes cause a reduction in water flow.
- Overhunting specific animal species is a threat to them, and they could be extinct in the future.
- Climate change due to greenhouse gas emissions is changing the rainfall patterns, altering species ranges and water and chemical cycles that define a current ecosystem.
Final Words:
Biodiversity means all different kinds of life present in an area. It includes a variety of plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms that make up the natural world. All the species of living organisms work together in ecosystems to maintain a balance and support life on Earth.
Everything that we need in nature, such as food, water, shelter, and medicine, relies on biodiversity. But human activities are putting more pressure on the planet and consuming natural resources.
As a result, the balance of ecosystems is at risk, and we are losing biodiversity. Therefore, it is necessary to take steps for the restoration of natural resources and keep our planet habitable.



